Import a project by git URL
Some features of dbt Cloud require a tight integration with your git host, for example, updating GitHub pull requests with dbt Cloud run statuses. Importing your project by a URL prevents you from using these features. Once you give dbt Cloud access to your repository, you can continue to set up your project by adding a connection and creating and running your first dbt Cloud job.
Don't see your git provider on this page? Please contact dbt Support - we're happy to help you set up dbt Cloud with any supported git provider.
In dbt Cloud, you can import a git repository from any valid git URL that points to a dbt project. There are some important considerations to keep in mind when doing this.
Git protocols
You must use the git@... or ssh:... version of your git URL, not the https://... version. dbt Cloud uses the SSH protocol to clone repositories, so dbt Cloud will be unable to clone repos supplied with the HTTP protocol.
Managing Deploy Keys
After importing a project by Git URL, dbt Cloud will generate a Deploy Key for your repository. To find the deploy key in dbt Cloud:
- Click the gear icon in the upper right-hand corner.
- Click Account Settings --> Projects and select a project.
- Click the Repository link to the repository details page.
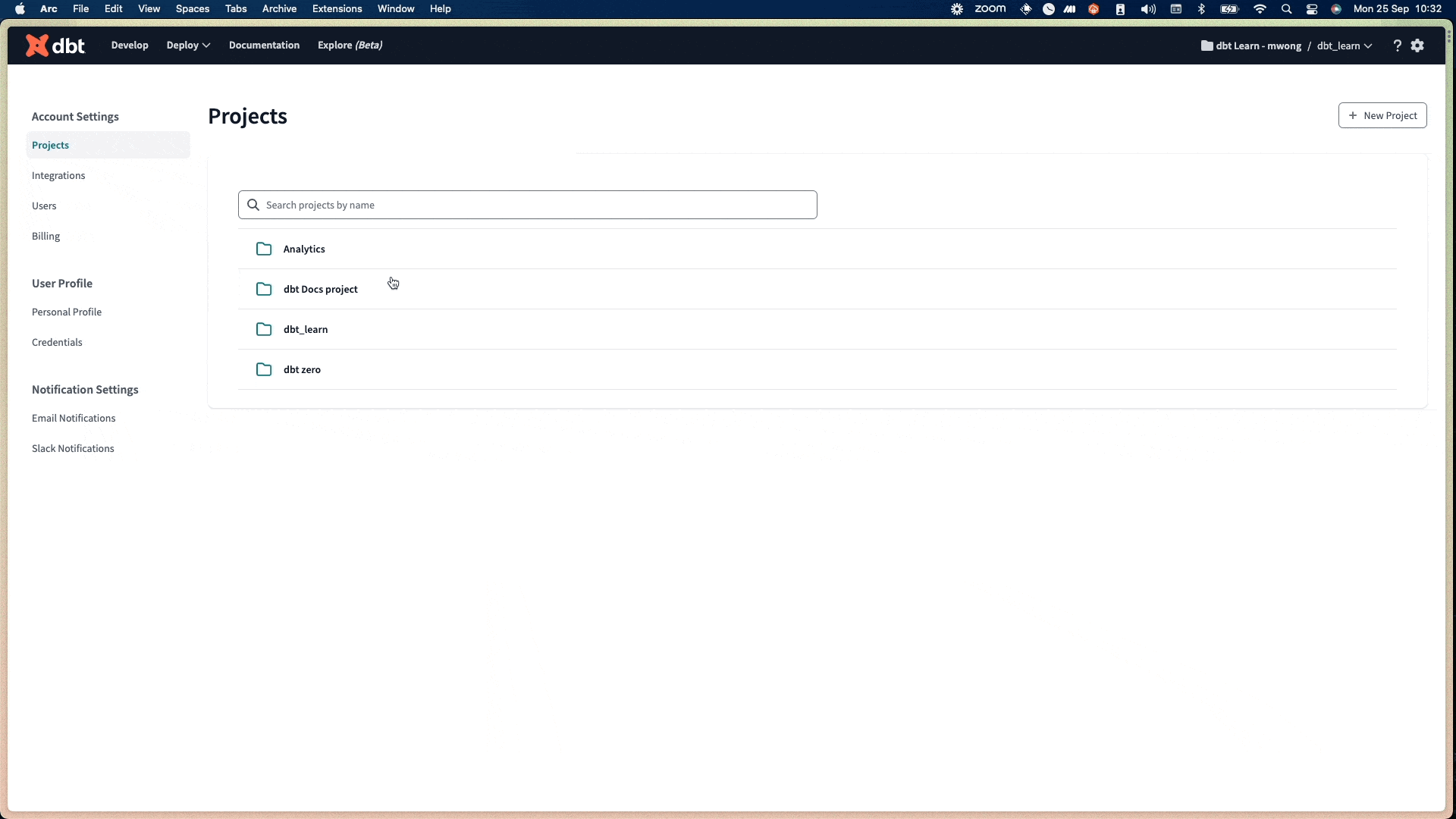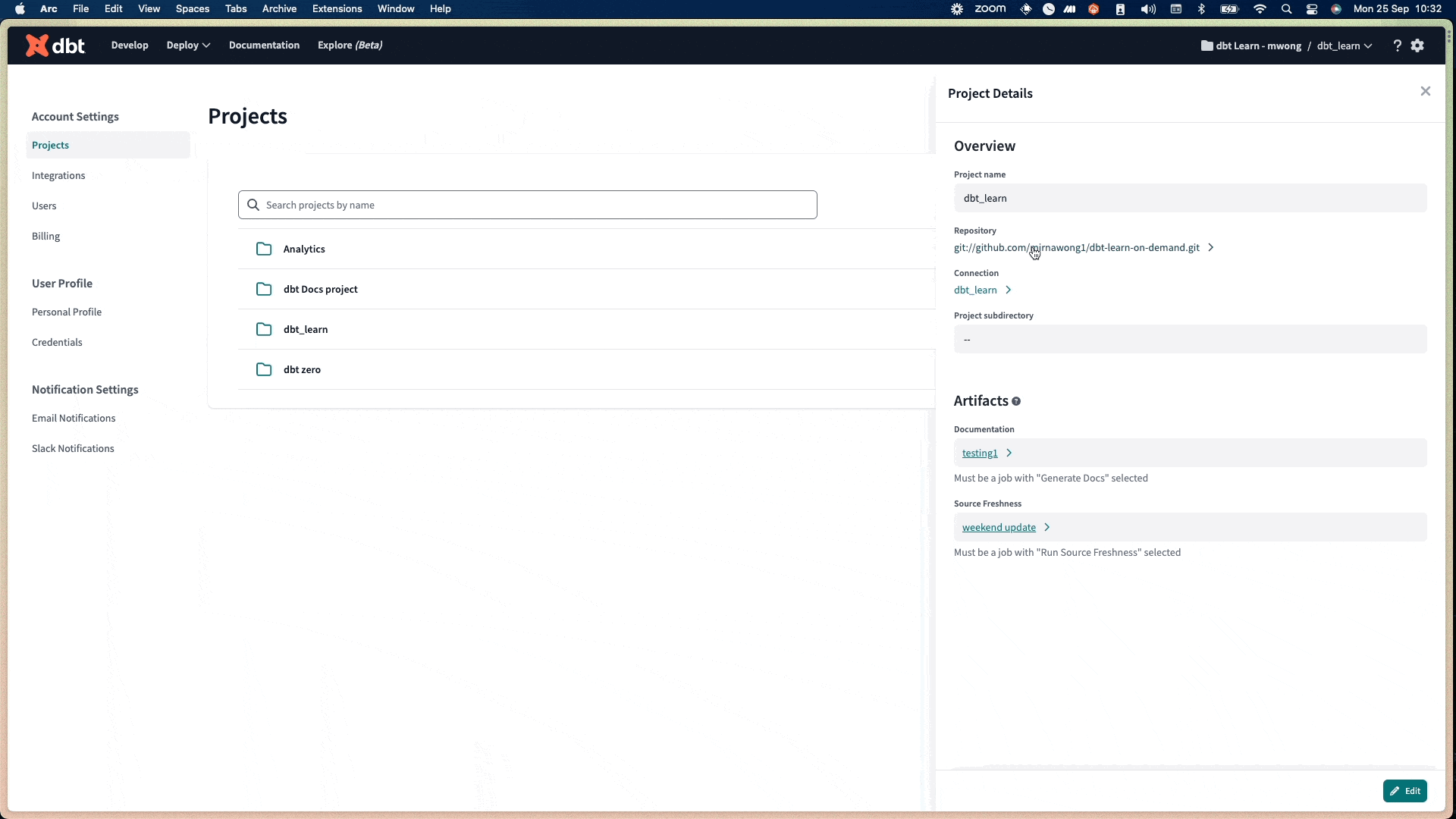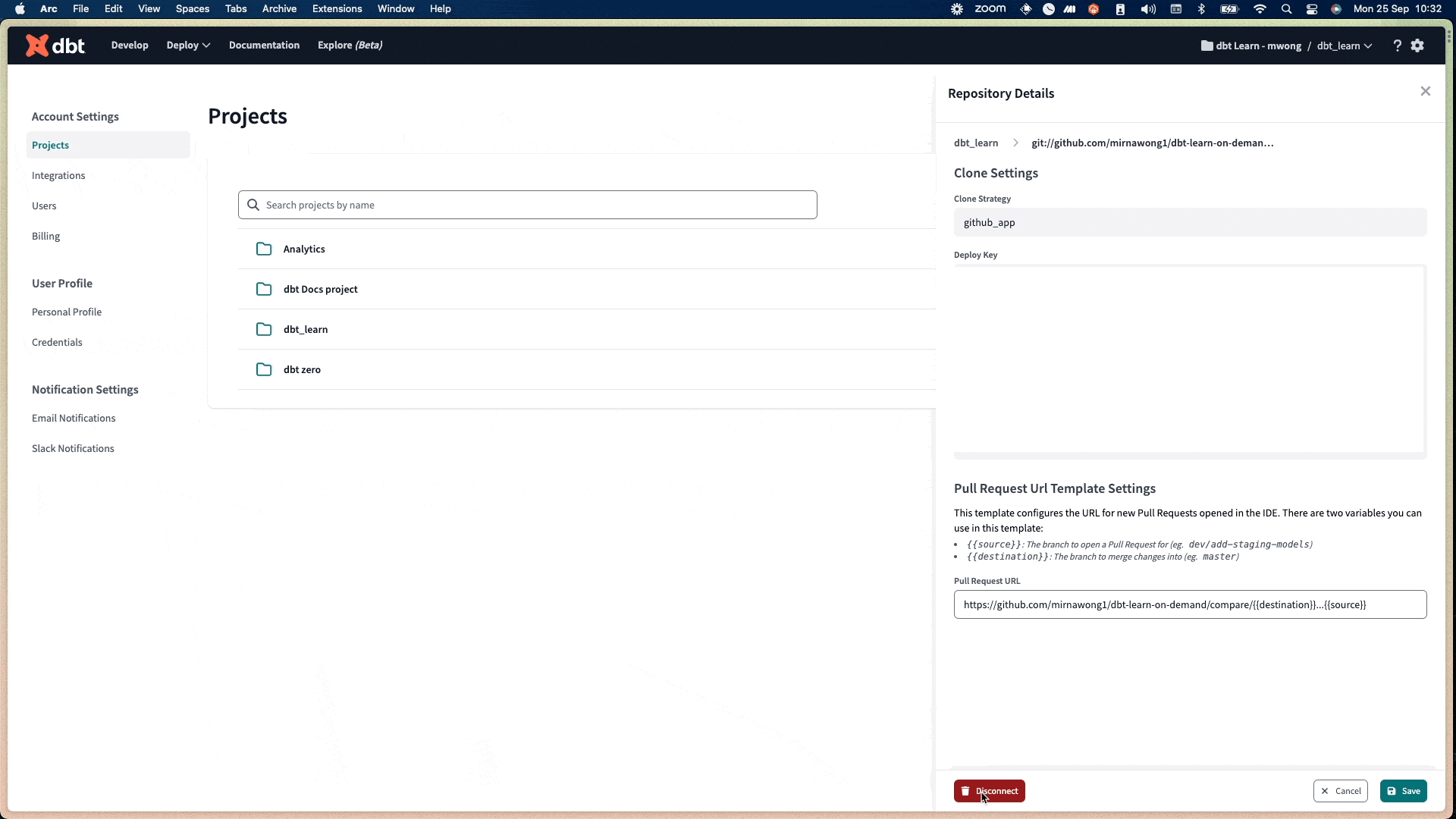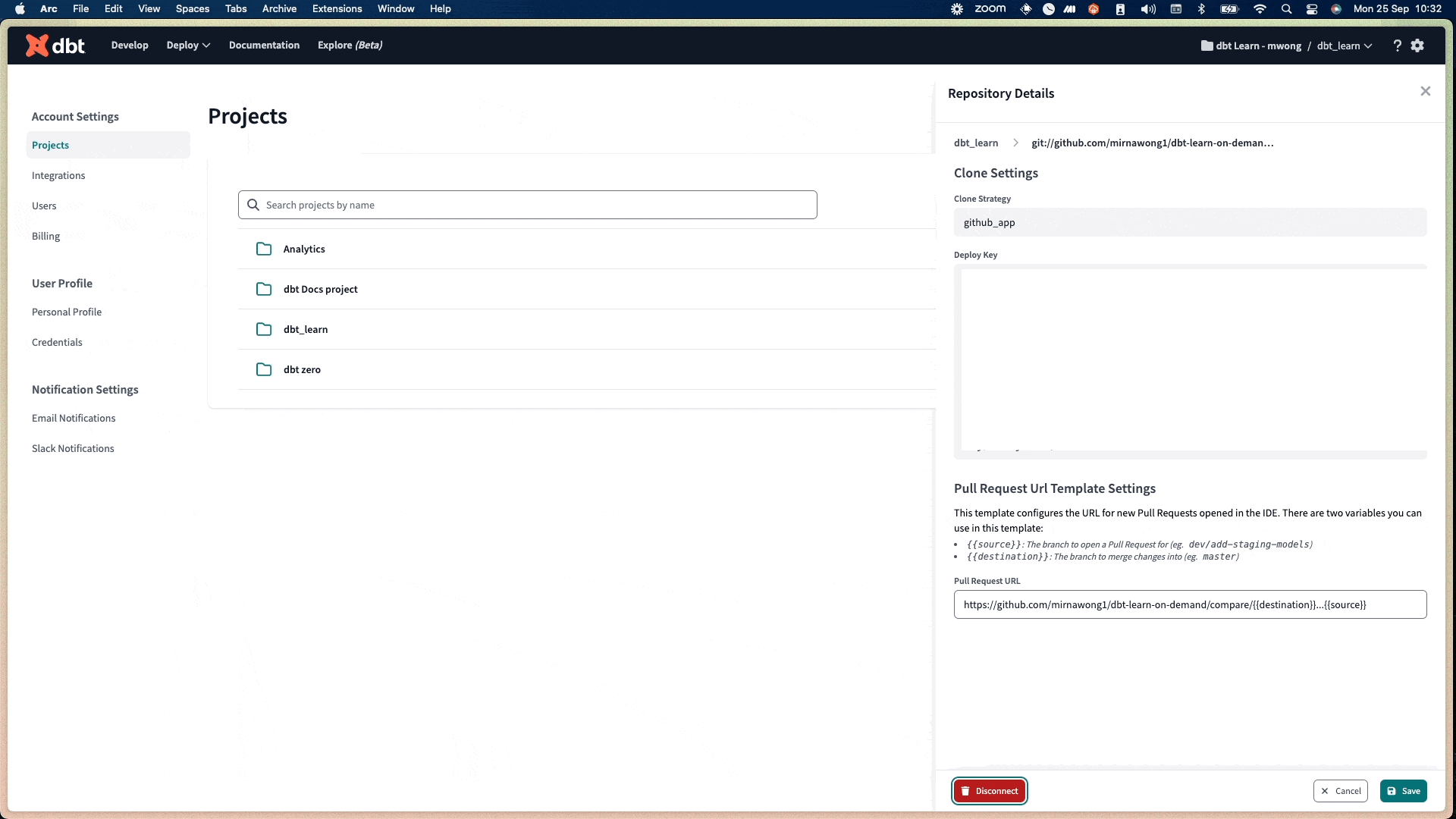
- Copy the key under the Deploy Key section.
You must provide this Deploy Key in the Repository configuration of your Git host. Configure this Deploy Key to allow read and write access to the specified repositories.
Note: Each dbt Cloud project will generate a different deploy key when connected to a repo, even if two projects are connected to the same repo. You will need to supply both deploy keys to your Git provider.
GitHub
If you use GitHub, you can import your repo directly using dbt Cloud's GitHub Application. Connecting your repo via the GitHub Application enables Continuous Integration.
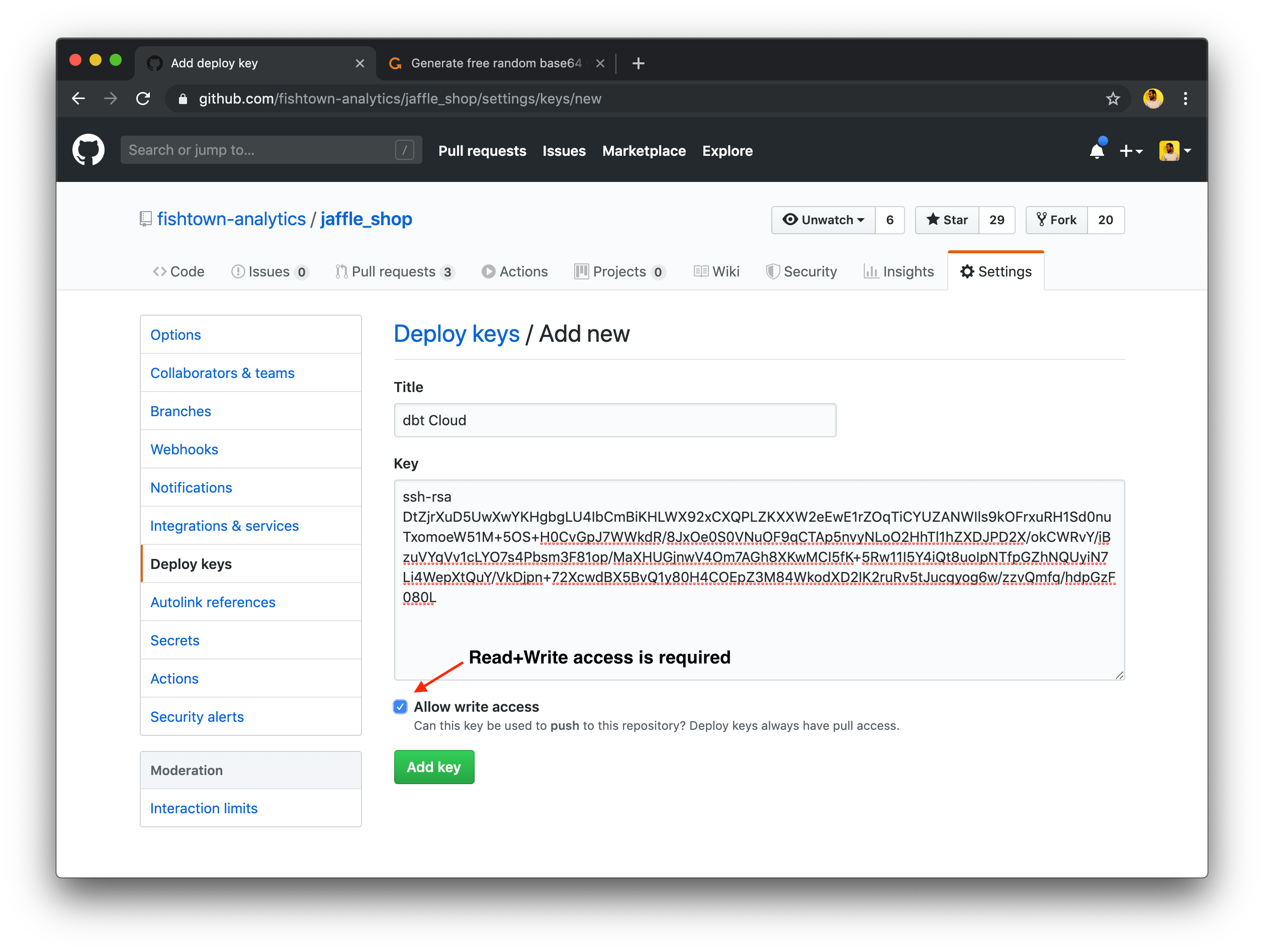
- To add a deploy key to a GitHub account, navigate to the Deploy keys tab of the settings page in your GitHub repository.
- After supplying a name for the deploy key and pasting in your deploy key (generated by dbt Cloud), be sure to check the Allow write access checkbox.
- After adding this key, dbt Cloud will be able to read and write files in your dbt project.
- Refer to Adding a deploy key in GitHub
GitLab
If you use GitLab, you can import your repo directly using dbt Cloud's GitLab Application. Connecting your repo via the GitLab Application enables Continuous Integration.
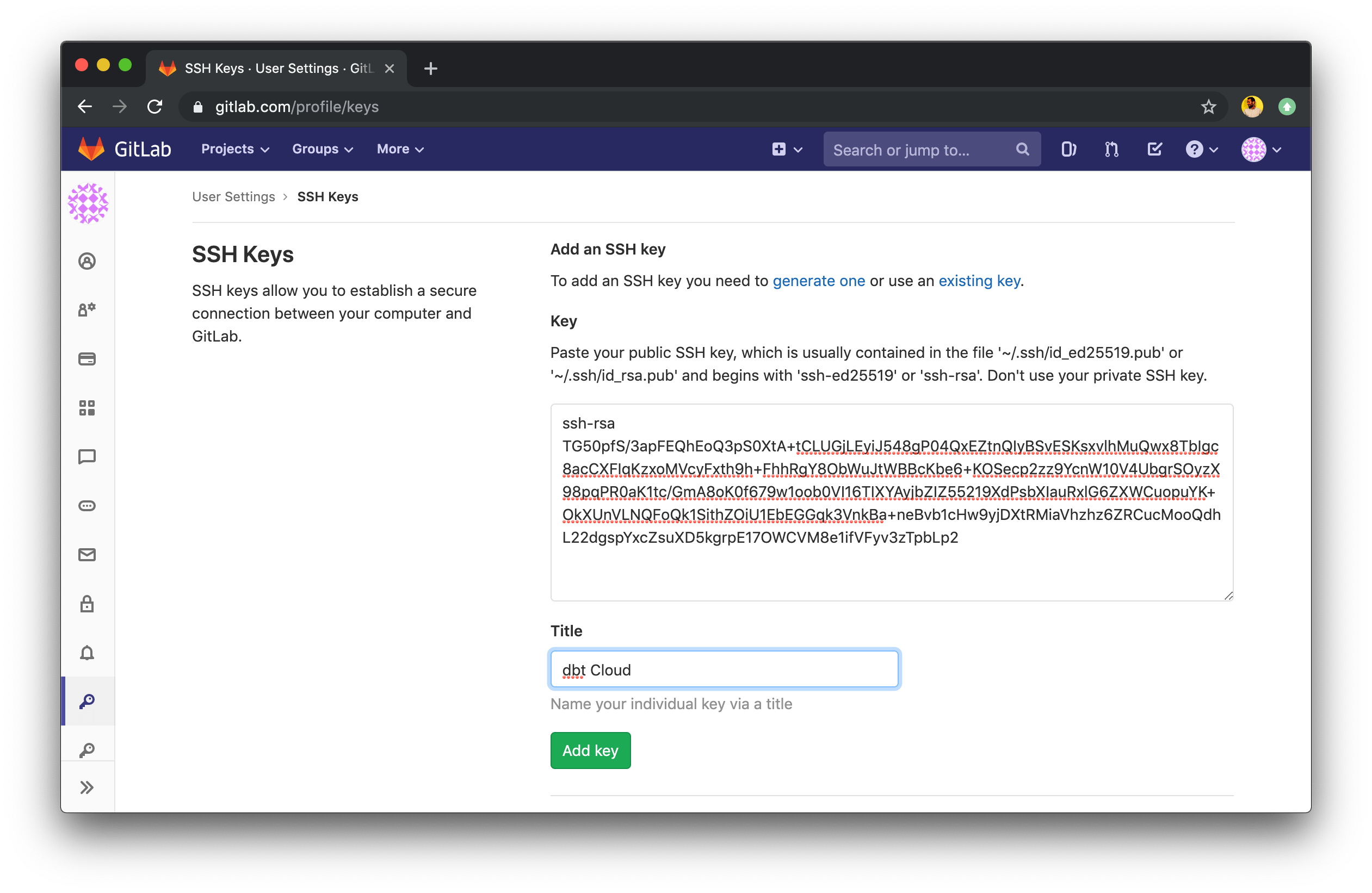
- To add a deploy key to a GitLab account, navigate to the SSH keys tab in the User Settings page of your GitLab account.
- Next, paste in the deploy key generated by dbt Cloud for your repository.
- After saving this SSH key, dbt Cloud will be able to read and write files in your GitLab repository.
- Refer to Adding a read only deploy key in GitLab
BitBucket
Use a deploy key to import your BitBucket repository into dbt Cloud. To preserve account security, use a service account to add the BitBucket deploy key and maintain the connection between your BitBucket repository and dbt Cloud.
BitBucket links every repository commit and other Git actions (such as opening a pull request) to the email associated with the user's Bitbucket account.
To add a deploy key to a BitBucket account:
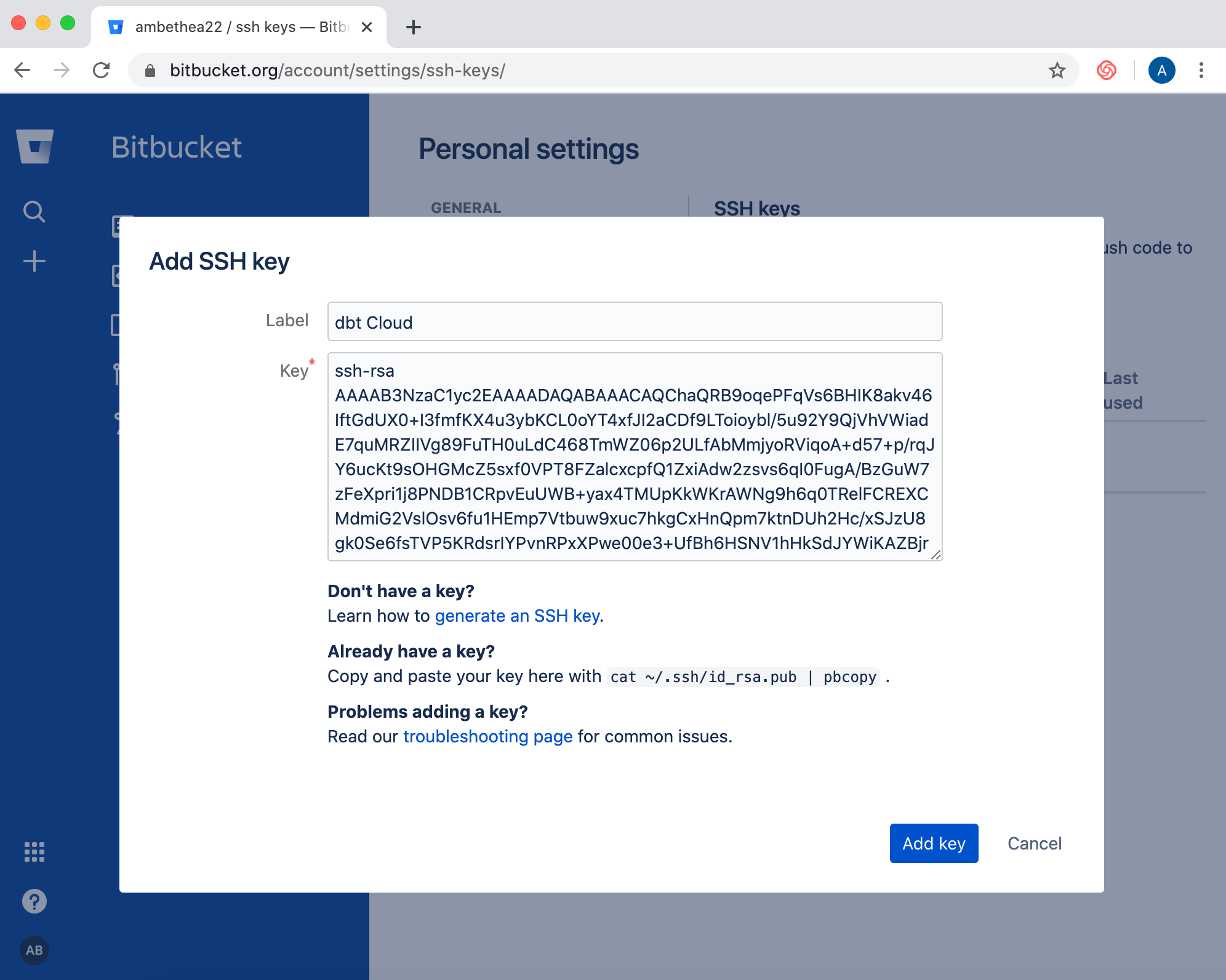
- Navigate to SSH keys tab in the Personal Settings page of your BitBucket account.
- Next, click the Add key button and paste in the deploy key generated by dbt Cloud for your repository.
- After saving this SSH key, dbt Cloud will be able to read and write files in your BitBucket repository.
AWS CodeCommit
dbt Cloud can work with dbt projects hosted on AWS CodeCommit, but there are some extra steps needed compared to Github or other git providers. This guide will help you connect your CodeCommit-hosted dbt project to dbt Cloud.
Step 1: Create an AWS User for dbt Cloud
- To give dbt Cloud access to your repository, first you'll need to create an AWS IAM user for dbt Cloud.
- Log into the AWS Console and navigate to the IAM section.
- Click Add User, and create a new user by entering a unique and meaningful user name.
- The user will need clone access to your repository. You can do this by adding the AWSCodeCommitPowerUser permission during setup.
Step 2: Import your repository by name
- Open the AWS CodeCommit console and choose your repository.
- Copy the SSH URL from that page.
- Next, navigate to the New Repository page in dbt Cloud.
- Choose the Git Clone tab, and paste in the SSH URL you copied from the console.
- In the newly created Repository details page, you'll see a Deploy Key field.
- Copy the contents of this field as you'll need it for Step 3.
Note: The dbt Cloud-generated public key is the only key that will work in the next step. Any other key that has been generated outside of dbt Cloud will not work.
Step 3: Grant dbt Cloud AWS User access
- Open up the newly created dbt Cloud user in the AWS IAM Console.
- Choose the Security Credentials tab and then click Upload SSH public key.
- Paste in the contents of the Public Key field from the dbt Cloud Repository page.
- Once you've created the key, you'll see an SSH key ID for it.
- Contact dbt Support and share that field so that dbt Support team can complete the setup process for you.
Step 4: Specify a custom branch in dbt Cloud
CodeCommit uses master as its default branch, and to initialize your project, you'll need to specify the master branch as a custom branch in dbt Cloud.
- Go to Deploy -> Environments -> Development.
- Select Settings -> Edit and under General Settings, check the Default to a custom branch checkbox.
- Specify the custom branch as
masterand click Save.
Step 5: Configure pull request template URLs (Optional)
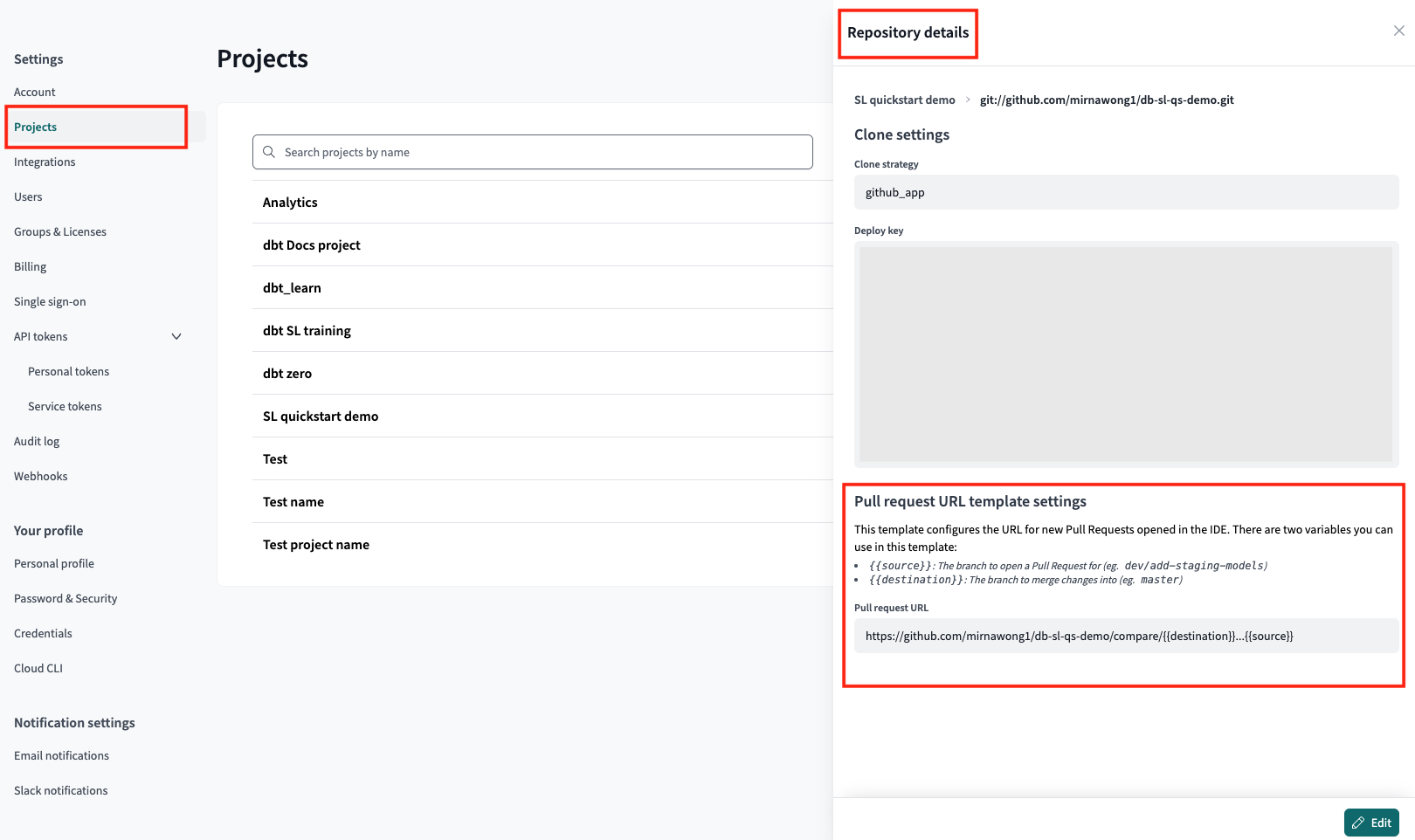
To prevent users from directly merging code changes into the default branch, configure the PR Template URL in the Repository details page for your project. Once configured, dbt Cloud will prompt users to open a new PR after committing and synching code changes on the branch in the IDE, before merging any changes into the default branch.
- Go to Account Settings -> Projects -> Select the project.
- Click the repository link under Repository.
- In the Repository details page, click Edit in the lower right.
- In the Pull request URL field, set the URL based on the suggested PR template format.
- Replace
<repo>with the name of your repository (Note that it is case sensitive). In the following example, the repository name isNew_Repo. - After filling the Pull request URL field, click Save.
🎉 You're all set! Once dbt Support handles your request and you've set your custom branch, your project is ready to execute dbt runs on dbt Cloud.
Azure DevOps
If you use Azure DevOps and you are on the dbt Cloud Enterprise plan, you can import your repo directly using dbt Cloud's Azure DevOps Integration. Connecting your repo via the Azure DevOps Application enables Continuous Integration.
-
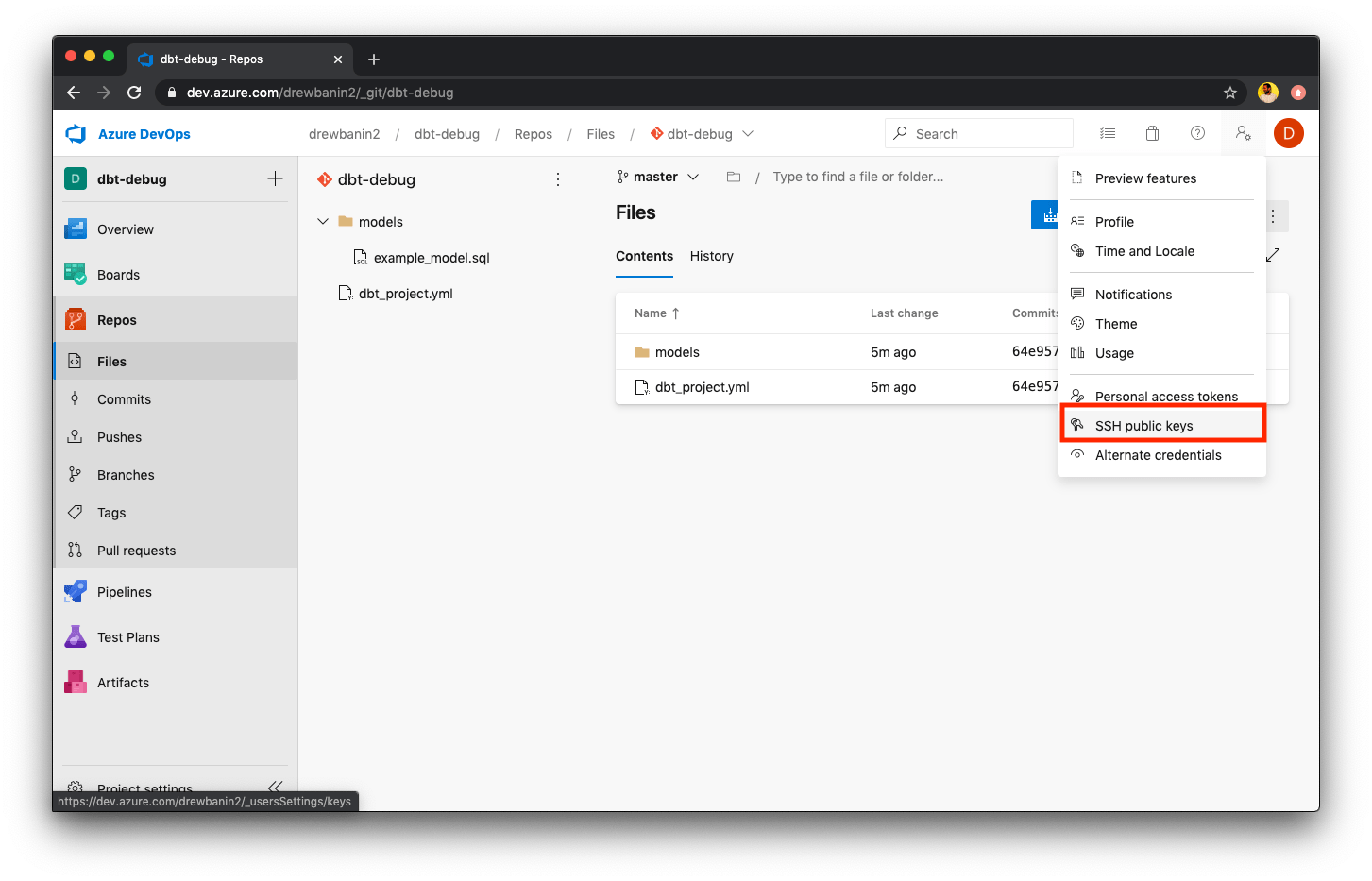
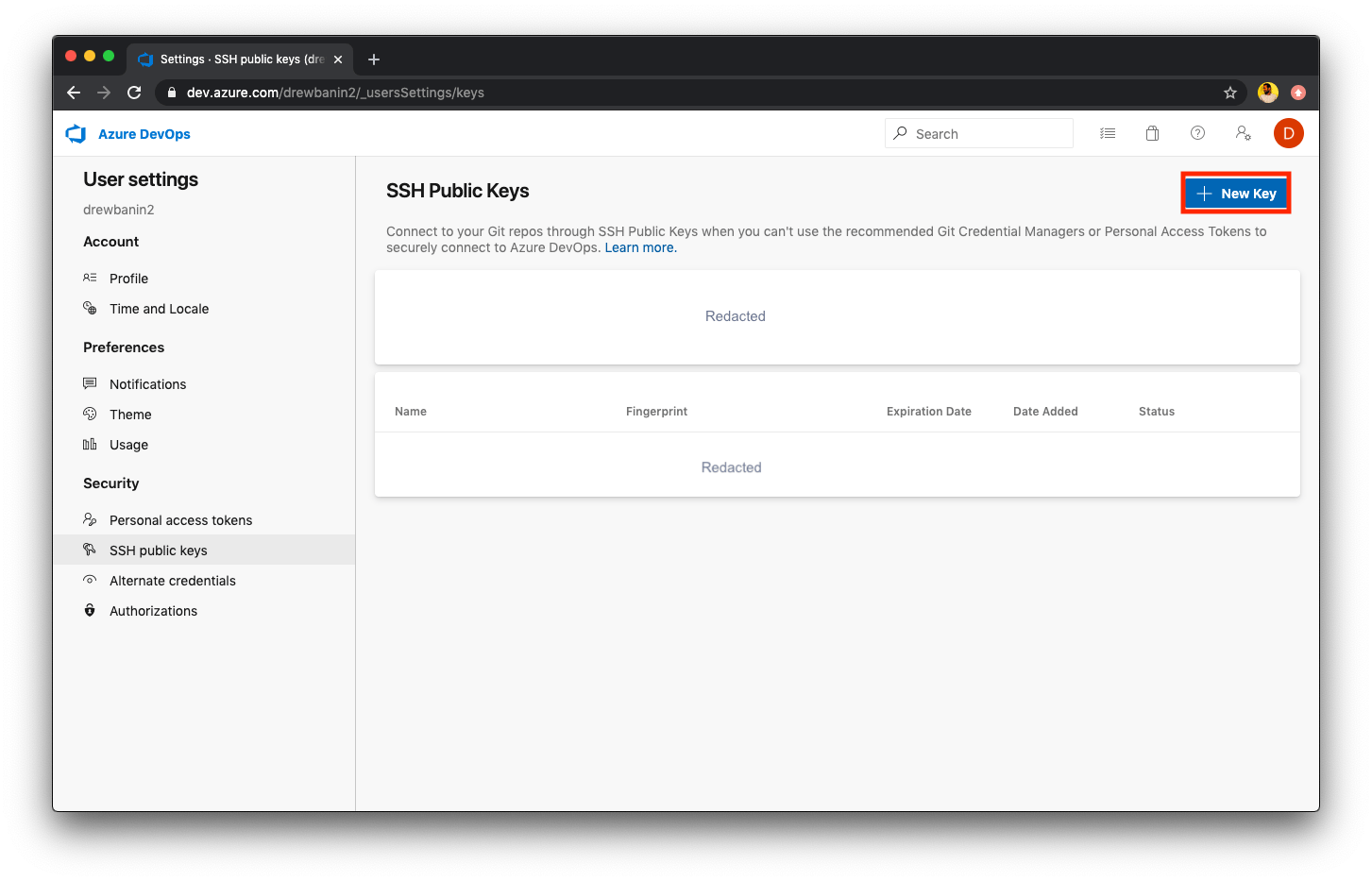
To add a deploy key to an Azure DevOps account, navigate to the SSH public keys page in the User Settings of your user's Azure DevOps account or a service user's account.
-
We recommend using a dedicated service user for the integration to ensure that dbt Cloud's connection to Azure DevOps is not interrupted by changes to user permissions.
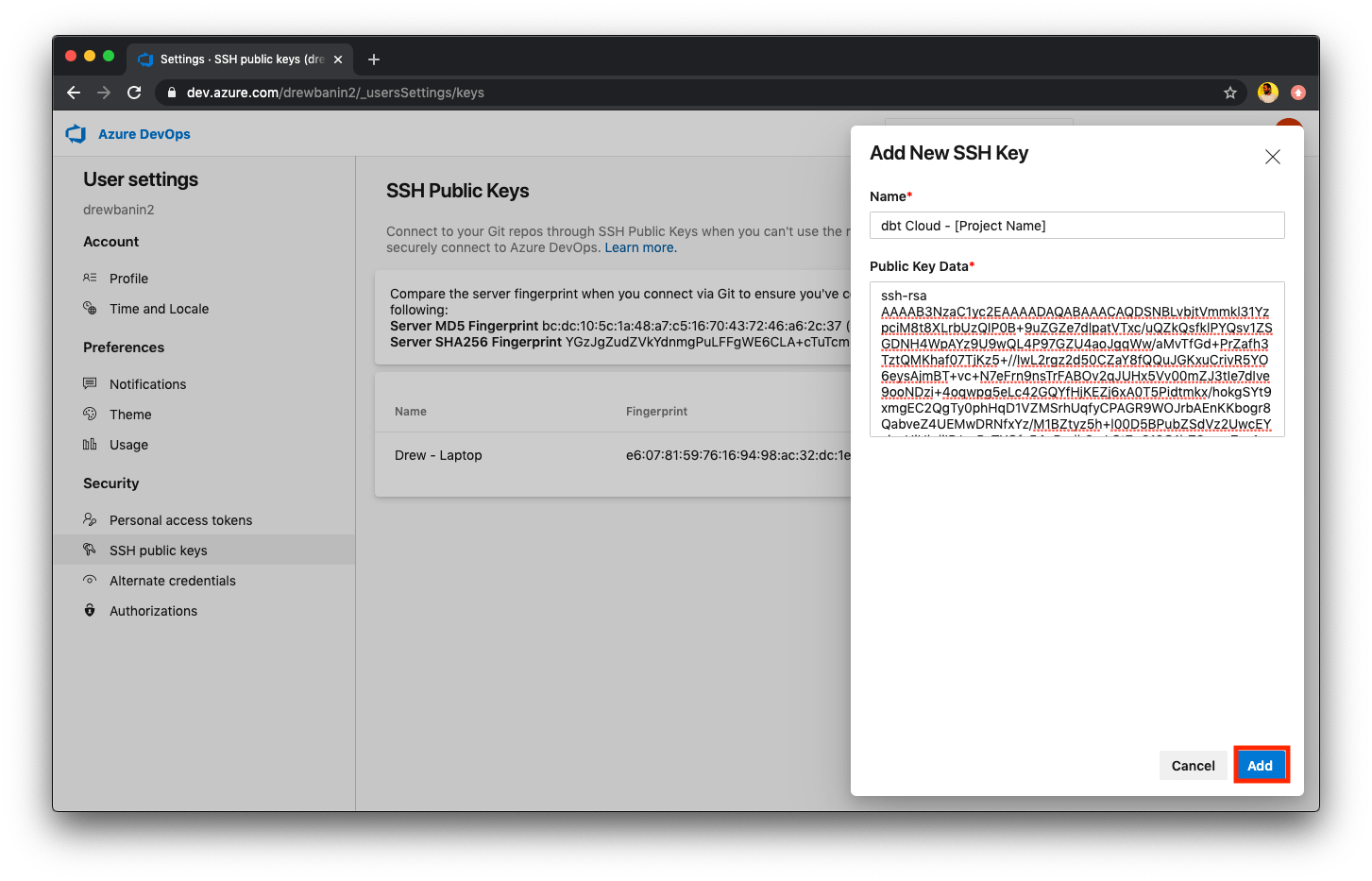
- Next, click the + New Key button to create a new SSH key for the repository.
-
Select a descriptive name for the key and then paste in the deploy key generated by dbt Cloud for your repository.
-
After saving this SSH key, dbt Cloud will be able to read and write files in your Azure DevOps repository.